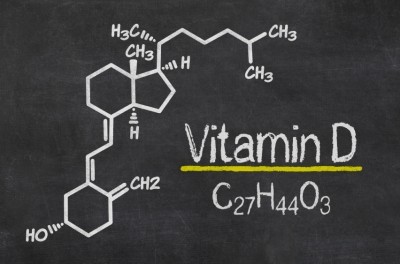
Extent of vitamin D’s role extends to easing IBS symptoms: Review

With links to other colorectal conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer, the review found a correlation between low vitamin D status and severity of IBS symptoms.
“The study provides an insight into the condition and, importantly, a new way to try to manage it,” said Dr Bernard Corfe, lead study author and senior oncology lecturer at the University of Sheffield.
“It is evident from the findings that all people with IBS should have their vitamin D levels tested and a large majority of them would benefit from supplements.”
IBS is a poorly understood condition with no single known cause and cure. Its link to vitamin D status follows a spate of recent media attention stemming from a report that found 8–24% of children and 20% adults in the UK were vitamin D deficient.
In response, the UK government’s Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN), issued advice suggesting adults and children needed to consume 10 micrograms (μg) of vitamin D each day either through supplements or diet.
Study details
Dr Coffe’s review gathered the seven studies that have been published to date, which investigate the role for vitamin D in IBS.
In the four observational studies included, the consensus reported a substantial proportion of the IBS population was vitamin D deficient.
Two intervention studies reported improvement in IBS symptom severity scores and quality of life (QoL) with vitamin D supplementation.
“The available evidence suggests that low vitamin D status is common among the IBS population and merits assessment and rectification for general health reasons alone,” the study concluded.
“An inverse correlation between serum vitamin D and IBS symptom severity is suggested and vitamin D interventions may benefit symptoms.
“However, the available RCTs do not provide strong, generalisable evidence; larger and adequately powered interventions are needed to establish a case for therapeutic application of vitamin D in IBS.”
Dr Coffe’s team commented on the limitations of their review highlighting the studies’ vitamin D status of the wider population was not reported.
In taking this into account, the cause and effect were difficult to determine as it could be argued that individuals with IBS may exhibit behaviour changes.
They cited the increased time spent indoors as a result of the symptoms as an example suggesting this could’ve impacted on vitamin D status.
“The body of evidence accrued across multiple populations already suggests that vitamin D status assessment should be incorporated as a routine assessment,” the review concluded.
“This could be done alongside IBS diagnosis in routine practice to identify individuals at risk and likely to benefit from vitamin D intervention for general health as much as for IBS symptoms.”
Establishing EU vitamin D status
Given existing national structures and systems, attempts to compare serum 25(OH)D and vitamin D deficiency prevalence have proved unfeasible for regulatory agencies.
Calls to establish the use of centralised laboratories to make international estimates more reliable have also gone unheeded.
Compounding the problem is the variability from different study outcomes that have seen vitamin D and serum 25(OH)D levels range from 10% to 300%.
Although there are many likely contributory reasons for differences in vitamin D deficiency prevalence estimates between populations, differences in analytic method for serum 25(OH)D are likely to contribute.
A number of research papers have shown available 25(OH)D assays can produce markedly differing results.
Source: European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Published online ahead of print, doi: 10.1038/s41430-017-0064-z
“Vitamin D status in irritable bowel syndrome and the impact of supplementation on symptoms: what do we know and what do we need to know?”
Authors: Claire Williams, Elizabeth Williams & Bernard Corfe