The molecule of interest is the vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM). Its genetic expression and production in the blood serum are key factors of headache severity.
Its production is induced by the presence of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha, which is also a vasodilator.
Medicines for migraine usually work by acting as an anti-inflammatory agent and preventing the production of TNF-alpha.
Writing in the BMC Research Notes, researchers from Iran said they have decided to trial the use of omega-3 and curcumin, since existing evidence showed that they could produce similar anti-inflammatory effects as migraine drugs.
In a two-month double-blinded clinical trial, 80 patients diagnosed with episodic migraine were randomised into the following four groups.
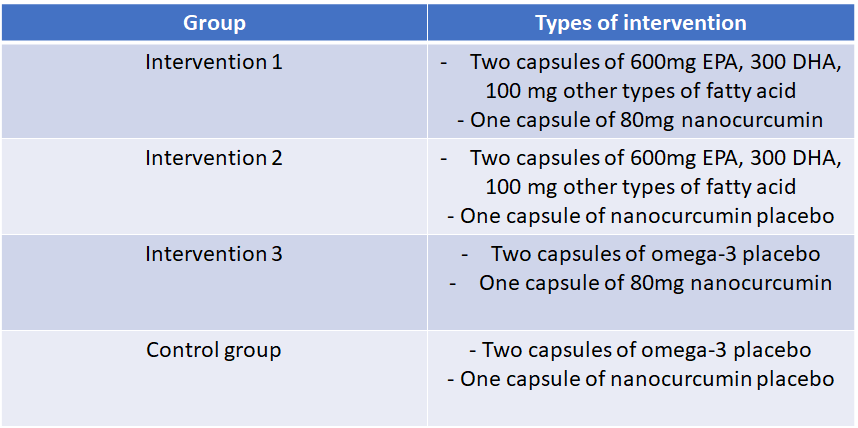
The omega-3 supplement and placebo were prepared by Zahravi Pharmaceutical Company, while the nanocurcumin supplement and placebo were prepared by the Sinacurcumin Pharmaceutical Company.
Subsequently, a questionnaire was used to record the incidence, duration, and severity of migraine amongst the trial participants.
Their blood samples and total RNA from cells were also collected to measure the blood serum and genetic expression of VCAM.
Combo works best
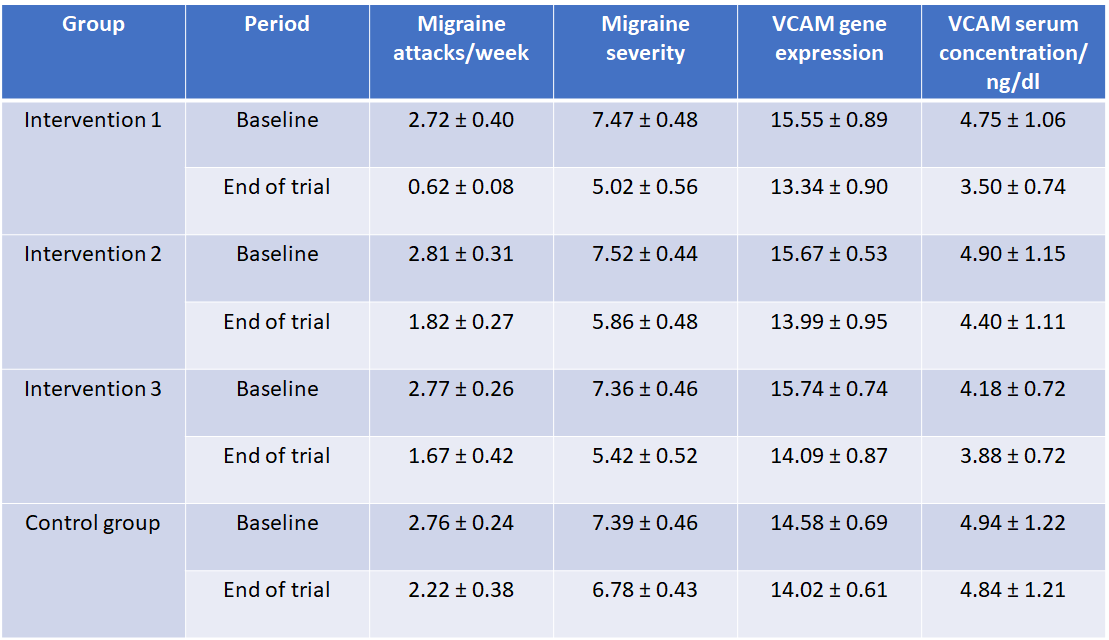
The combination of omega-3 and nanocurcumin (intervention group 1) had produced the best results, although the supplementation of omega-3 (intervention group 2) alone also significantly reduced VCAM genetic expression and the incidence and severity of migraine.
A statistically borderline significant improvement – where the p-value was larger than 0.06, slightly higher than 0.05 – was seen in the group taking only nanocurcumin (intervention group 3).
For example, in the group taking both omega-3 and nanocurcumin, the number of migraine attacks per week decreased from 2.72 ± 0.40 to 0.62 ± 0.08.
For the group taking only omega-3, the number of headache attacks per week was down from 2.81 ± 0.31 to 1.82 ± 0.27.
At the genetic level, the expression of VCAM in group 1 dropped from 15.55 ± 0.89 to 13.34 ± 0.90, a significant change where the p-value was 0.001.
As for group 2, the genetic expression of VCAM decreased from 15.67 ± 0.53 to 13.99 ± 0.95, also a significant change where the p-value was 0.05.
Table of findings
“It appears that the W-3 (omega-3) and combined W-3 and nanocurcumin can relieve VCAM serum level and its gene expression in patients with episodic migraine.
“Moreover, the combination of W-3 with nanocurcumin might cause more significant declines in VCAM level in the serum of migraine patients than when W-3 is administered alone,” the researchers concluded.
However, they also pointed out that the findings contradicted with a previous study by Poreba et al, where omega-3 had no effect on serum VCAM concentration in obese population.
Another meta-analysis also reported no meaningful effect of omega-3 on serum VCAM concentration.
The researchers explained that these results could be due to differences in the study duration, population and omega-3 dosage.
Explanation
Both omega-3 and nanocurcumin have brought about the improvements by downregulating several factors.
For instance, omega-3 could have worked by inhibiting factors involved in the formation of VCAM.
“Experimental studies have demonstrated W-3 suppress VCAM-1 expression by inhibition of PPAR-γ, IRF-1 and miR-126 expression, sirtuin-1 production and nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha (IκBα) and NFKB phosphorylation, which are involved in vascular adhesion molecules formation,” the researchers said.
The omega-3 fatty acids could also inhibit macrophage activity and decrease VCAM-1 levels, in turn attenuating the severity of migraine headaches.
On the other hand, curcumin also reduce VCAM production by downregulating several factors, including “the phosphorylation of PI3-kinase/Akt, p38 MAPK and JNK and NFKB expression, the migration and proliferation T-cells, induction of anti-oxidative enzymes and reduction of the expression and transcriptional activity of histone acetyltransferases including AP-1 and p300.”
Source: BMC Research Notes
The omega-3 and Nano-curcumin effects on vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM) in episodic migraine patients: a randomized clinical trial
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-021-05700-x
Authors: Abdolahi, M., Karimi, E., Sarraf, P. et al.





