Researchers from the University of Colorado aimed to investigate if exercise reduced calcium level and increased parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in post-menopausal women. Such changes were previously observed in young, male athletes and were found to cause reduced bone density over time.
Study details
In a randomised, double-blind, cross-over study 33 women aged 57-65 were divided into two groups. In the first group 10 women consumed sports drink supplement with 1000mg calcium an hour before exercise or a placebo drink.
In the second group 23 women consumed sports drink supplement with 1000mg calcium (Aquamin supplied by Irish supplier Marigot) 15 minutes before exercise or placebo.
In both groups women continued drinking throughout the hour-long moderate exercise (brisk walking).
Results
The study results suggested calcium supplementation prevented calcium decrease and reduced PTH and bone reabsorption (CTX) increases when consumption began an hour before exercise.
When the supplementation began only 15 minutes before exercise calcium decrease was reduced but not eliminated and the levels on PTH and CTX were not affected.
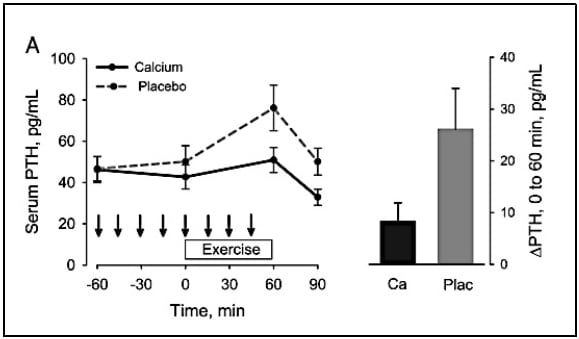
“This suggests that the timing of Ca supplementation before exercise plays an important role in regulating changes in Ca homeostasis during exercise. These results in postmenopausal women during vigorous treadmill walking are consistent with those observed previously in young male road cyclists,” said the researchers.
“The finding that Ca supplementation during exercise attenuated increases in CTX suggests that the disruption in Ca homeostasis can be minimized when Ca is available to be absorbed from the gut,” they added.
Aquamin is a marine-sourced form of calcium that included magnesium and 72 other trace minerals.
Source:
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise
DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000320
'Calcium Supplementation and Parathyroid Hormone Response to Vigorous Walking in Postmenopausal Women'
K.Shea, D.Barry, V. Sherk et al.
