Promotional Features
Yeast protein has great potential in sports nutrition applications
With the global population explosion, the demand for high-quality protein increases rapidly. The world’s population is projected to grow to 9.7 billion by 2050, of which two-thirds are projected to live in urban areas [1]. This increase in population combined with rapidly changing eating habits are creating a substantial “protein gap” between the protein available and the expected demand in 2050.
According to FMCG Gurus [2], sports nutrition products are more popular than ever before. People are looking to improve their overall health and are actively looking for “better for me” products. High protein and low sugar alternatives to traditional snacking products are becoming a big opportunity for many brands and manufacturers. Consumers want guilt-free products that offer a nutritional boost and functional benefit to help get them through the day. According to Euromonitor International [3], sports nutrition is expected to outpace the broader set of nutritionals through 2023 at an 8% global CAGR, compared to less than 3% CAGR for other adjacent nutritional categories.
Opportunities within Sports Nutrition
With consumers increasingly looking for multi-functionality in the products they choose, it is crucial for brands and manufacturers to meet the physiological, emotional and health needs of today’s demanding consumers. Having the right ingredients can open up more options in new product concepts to meet those needs. For companies competing in the Sports Nutrition category, this means offering products that not only support muscular recovery and reduce muscle fatigue, but also provide other health benefits to the consumers. Companies that are able to successfully meet such demands will be able to differentiate themselves from their competition and cement their position as leaders in the industry.
In order to determine how the different protein sources fared on sports nutrition, a series of experiments were conducted by researchers from Angel Human Health. Here’s what they found:
Yeast protein - High-quality protein source
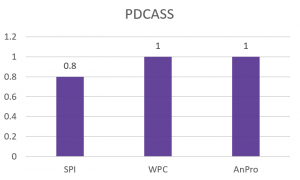
Containing complete essential amino acids, yeast protein is a high-quality protein source with high bioavailability. The PDCAAS△ of yeast protein is in the same level as WPC (whey protein concentrate), higher than SPI (soy protein isolate)[4]. (SPI is a typical and widely used protein source from plants, the nutrition value of SPI is similar to pea protein.)
PDCASS of different protein sources
(Note: AnPro is the brand name of yeast protein in Angel Human Health, the same as in the following contents)
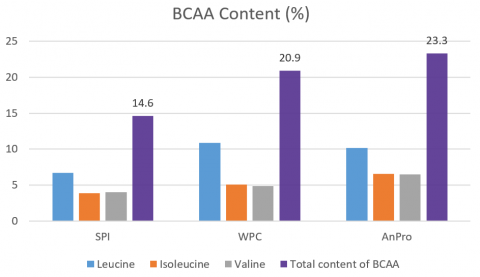
Besides, yeast protein contains significant amounts of branched chain amino-acids (BACC), Leucine, Isoleucine and Valine, which play an important role in muscle protein synthesis. Experimental results [5] showed that yeast protein contains 23.3% BCAA, much higher than both SPI and WPC. Yeast protein is the best protein for sports nutrition, which supports muscular recovery and reduces muscular fatigue.
Branched chain amino-acids (BACC) content in different protein sources
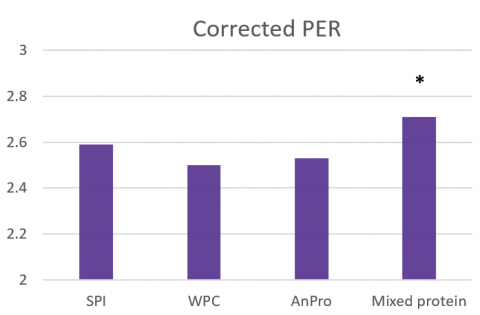
Furthermore, as a microbial-source protein, yeast protein is a good complement for proteins originated from plants and animals. Experimental results [4] showed that mixed protein (AnPro:WPC:SPI=1:1:1) can increase the digestion and absorption rate of proteins. This is called Protein Complementary Action†.
Corrected PER (Protein Efficacy Ratio) of different protein sources
Note: Compared with AnPro, * means P<0.05.
PER (Protein Efficacy Ratio) indicates the amount of weight gain per gram of protein consumed. According to international AOAC regulation, proteins with PER above 2.0 are considered to be of high quality protein sources.
Yeast protein - Slow-digesting protein
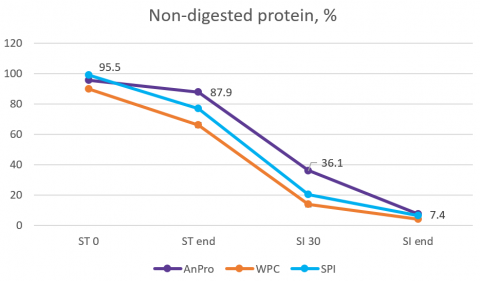
Experimental results of study using SHIME in vitro simulator [5] showed the digestion rate of yeast protein in the stomach and small intestine were significantly lower than WPC and SPI, while the digestion rate of the three protein sources were similar in the end of the small intestine. This means yeast protein is a slow-digesting protein, which may be helpful to anti-metabolism or muscle protection. Besides, slow-digesting protein can provide a stable flow of amino acids to prevent muscle tissue breakdown. Comparing to WPC and SPI, yeast protein can increase satiety and provide amino acid continuously and steadily, thus making yeast protein a good protein source for dieters and sport nutrition.
Not-digested protein content during the study using SHIME in vitro simulator
Note: ST 0: At the beginning of gastric digestion; ST end: end of gastric digestion; SI 30: small intestine after 30 min; SI end: end of small intestine.
Yeast protein - Gut-healthy protein
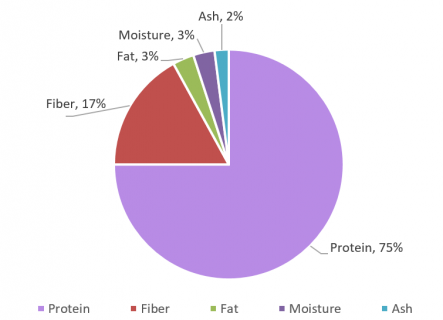
In addition to containing more than 75% high-quality protein, AnPro yeast protein also contains 17% of excellent fiber [4], which is good for gastrointestinal health and overall health.
Composition of AnPro yeast protein
The results of issued studies [4] showed that yeast protein can affect the composition of the intestinal flora and increase the diversity of intestinal flora, and it also can significantly reduce the declines of intestinal function caused by aging.
AnPro Yeast Protein has a great potential in Sports Nutrition applications
As a microbial-source protein, which is reliable, sustainable and eco-friendly [6], AnPro yeast protein is positioned to close the protein gap. Because of the multi-advantages of AnPro yeast protein for its nutrition and functions, such as high quality, slow-digesting and gut-healthy, AnPro yeast protein has a great application potential and is suitable to be widely applied in healthy foods to provide high-quality protein, especially in sports nutrition, such as muscle gainer, weight management products, energy bars, etc. The applications of AnPro yeast protein will be much wider in the near future, with more nutrition and function benefits be disclosed.
Yeast, the earliest domesticated microorganism in human history, is also the only microorganism with an annual yield of more than 1 megaton on this planet. With the continuous increase of human demand for proteins and the restriction of the earth’s resources for producing animal and plant proteins [6], AnPro yeast protein, as a representative source of microbial proteins, will play a more important role in the process of maintaining human health and sustainable development of the earth.
Read the earlier published article about AnPro Yeast Protein: AnPro Yeast Protein: Finding a sustainable solution for the protein gap
Reference
[1] United nations, populations division.
[2] How Sports Nutrition is Evolving in 2020.
[3] The Expansion of Sports Nutrition 2019.
[4] Internal data from Angel Yeast
[5] Chen Zhixian, Zhang Haibo, et al. Amino acid composition analysis and in vitro dynamic digestion of protein with three different sources. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition). 2019,40(2): 62-68.
[6] AnPro Yeast Protein: Finding a sustainable solution for the protein gap. (https://www.nutraingredients.com/News/Promotional-Features/AnPro-Yeast-Protein-Finding-a-sustainable-solution-for-the-protein-gap)
△PDCAAS: Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acids Score, is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans and their ability to digest it. The PDCAAS rating was adopted by the US FDA and the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization in 1993 as "the preferred best" method to determine protein quality.
†The amino acids contained in proteins from different sources can complement each other, which is called Protein Complementary Action. In order to maximize the protein complementary action, the biological species of protein sources should be as far away as possible. That is why scientists recommend people choose proteins from diversified sources, such as plant and microbial protein sources together in one meal.
If you need more information about AnPro yeast protein, please contact us at nutritech@angelyeast.com